In a highly digital era, an online presence is crucial to the success of a business. For many companies, their website is the flagship for most of their digital and inbound marketing efforts. It’s where potential customers, clients, vendors, and partners can find them, learn about their company, and contact them. It can be an access point for digital resources as well.
Precisely because of their importance, websites are a favorite target of cybercriminals. So that your website remains a profitable investment, you need to protect it from common cyberattacks. In this article, you’ll learn about the three most common cyberattacks, as well as their corresponding preventative measures.
1. Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks
Much like in a traffic jam where too many vehicles block the road and prevent movement, a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack freezes your website by sending too many visits or website requests.
This is executed by using several rogue computers and devices, resulting in your website not being able to handle all the requests at once, shutting it down. What’s worse, the excess traffic can overload your network and server, causing shutdowns, crashes, and further disruptions to normal operations.
SYN flood, Teardrop, Smurf, Ping of Death, and Botnet attacks are the five most prevalent DDoS attacks. To defend your website, have your network administrator, IT support services team, or managed services provider (MSP) do the following:
- Proactively monitor networks for any unusual activity.
- Optimize your network infrastructure with the goal of distributing network traffic evenly.
- Perform an assessment of your systems for potential exploits and misconfigurations.
- Always install the latest security patches for your software and hardware.
- Disable IP-directed broadcasts from your router or ensure your system is set to not to respond to these broadcasts.
Don’t take cybersecurity for granted!
Devise a cybersecurity strategy that fits your business by reading our free eBook: 3 Essential types of cyber security solutions your business must have.
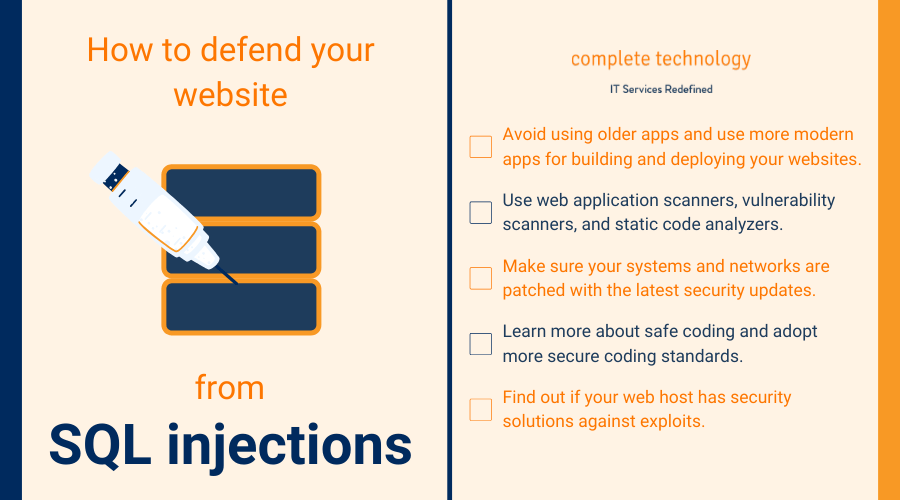
2. SQL injections
Traditional input fields such as passwords are typically harmless features on websites. But SQL injections, the most common form of website attack, use these page sections to exploit a website’s SQL software and create havoc on the site’s database.
Using this attack method, a hacker can make all sorts of inconvenient or harmful activities happen on your site, such as redirecting your site’s visitors to a malware-infected page. And if they choose, they can simply shut it down.
A hacker can even use this attack to access your site’s root server operating system and database. For instance, if you use your site to engage in commerce, gaining access to its database means a cybercriminal can view sensitive information, such as customer credit card numbers.
These are what you can do to protect your website.
- Avoid using older applications, such as J2EE and ASP.NET, and use more modern applications for building and deploying your websites.
- Use web application scanners, vulnerability scanners, and static code analyzers. They test your website applications for vulnerabilities, helping you ensure that they are secure.
- Make sure your systems and networks are patched with the latest security updates.
- Learn more about safe coding and adopt more secure coding standards. Some excellent ones are endorsed by the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP).
- Find out if your web host has security solutions against exploits. Cheap web hosting services usually don’t have security as a core feature, so avoid them.
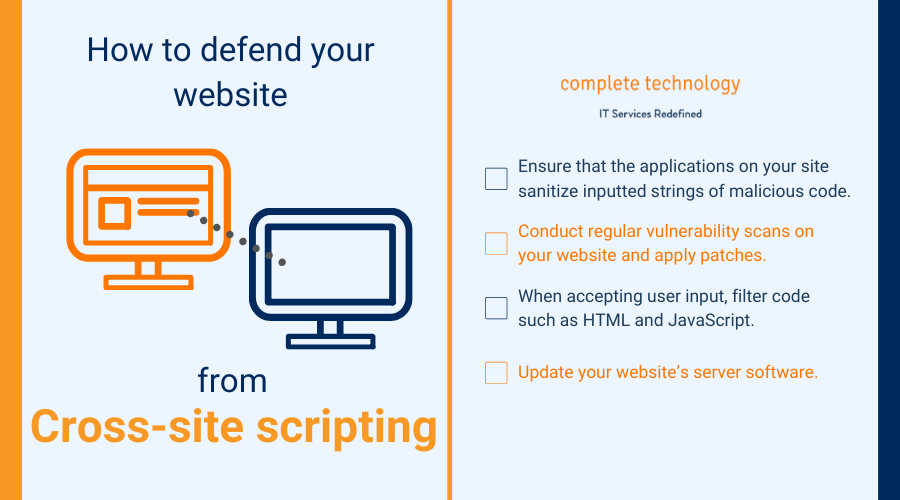
3. Cross-site scripting (XSS)
XSS is a security vulnerability found in website features like search bars, user forms, and comment boxes. As with SQL injections, hackers input malicious code into these features. But instead of causing damage to your site, they use this code to invade your site’s visitors.
Your site remains relatively unharmed, with the worst effect being lower click-through rates. However, the hacker has essentially turned your site into a trap, using it to gain access to your visitors’ computer systems.
Hackers can then perform malicious activities, such as recording a visitor’s keystrokes, viewing their sensitive information, stealing or destroying their files, and gaining control of their computer’s camera.
Here’s what you can do as a website owner to protect your site’s visitors from danger:
- Ensure that the applications on your site sanitize inputted strings of malicious code.
- Conduct regular vulnerability scans on your website and apply patches or fixes to its applications.
- When accepting user input, filter code such as HTML and JavaScript.
- Update your website’s server software.
At Complete Technology, we know how important it is for a business to protect its IT assets. That’s why we offer a comprehensive suite of cybersecurity strategies against hacking, data theft, phishing, and other emerging cyberattacks. Learn more about our security offerings by downloading this free ebook.